Updated: January 30, 2026
Written by Dan Simms
Nieves Martinez is a writer and editor at Fixr.com, specializing in home improvement and construction content. With over five years of experience and a Master's degree in Digital Marketing, she collaborates with industry professionals to create clear, carefully reviewed cost guides and renovation resources that help homeowners make informed remodeling decisions.
Learn moreReviewed by Nieves Martinez
Under current federal law, the Residential Solar Tax Credit (ITC) ended for customer-owned systems on December 31, 2025. As a result, solar panels, solar shingles, and battery systems placed in service in 2026 or later are not eligible for the 30% federal tax credit when homeowners own the system. Third-party owned systems (such as solar leases or PPAs) may still qualify under commercial credits, with savings sometimes passed on through lower rates.
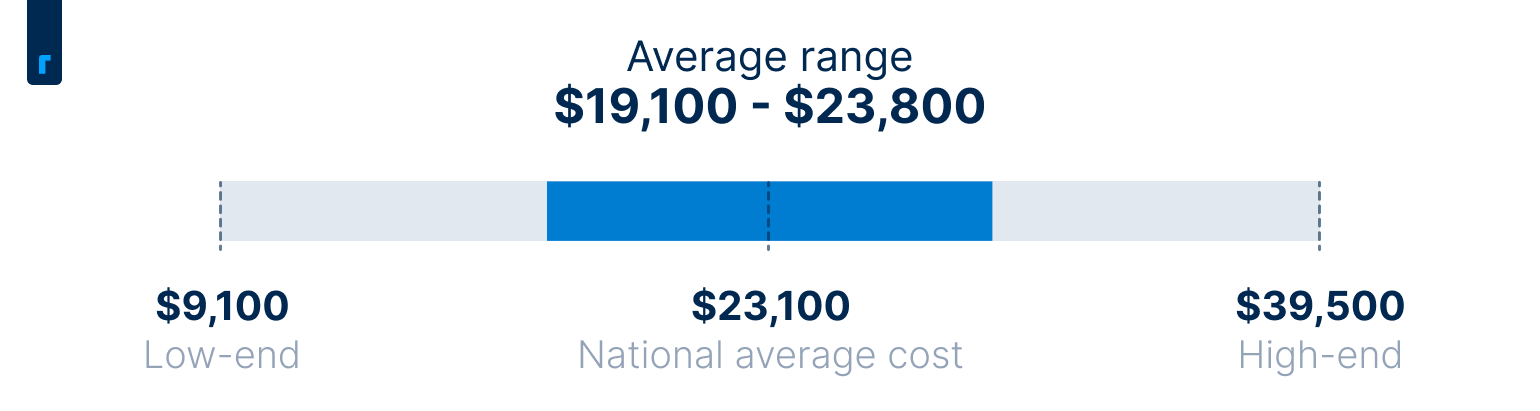
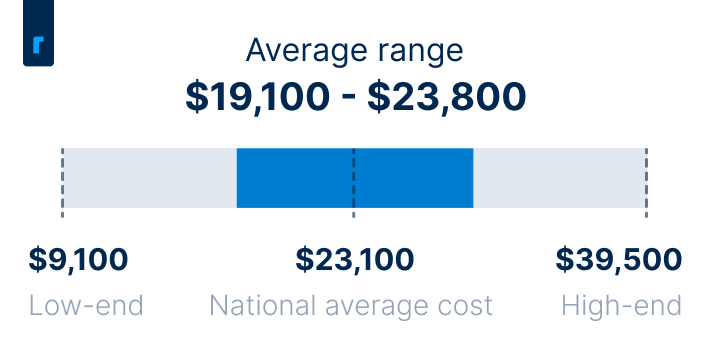
The average cost of installing a 7.6kW solar system on your roof is $23,100, and most homeowners pay somewhere between $19,100 and $23,800. Prices vary widely based on factors like the size of the system you need, the quality of the equipment you choose, how you pay for your system, any add-ons you choose, and more. Your location and access to local incentives can also have a major impact on your all-in costs.
Going solar can be an outstanding investment, not just for increased sustainability and environmental friendliness, but also for your wallet. A properly-sized solar array can drastically reduce your carbon footprint and can come close to eliminating your electric bill, providing substantial utility bill savings over time.
Cost of Solar Panel Installation
Solar Panel Installation Cost Breakdown
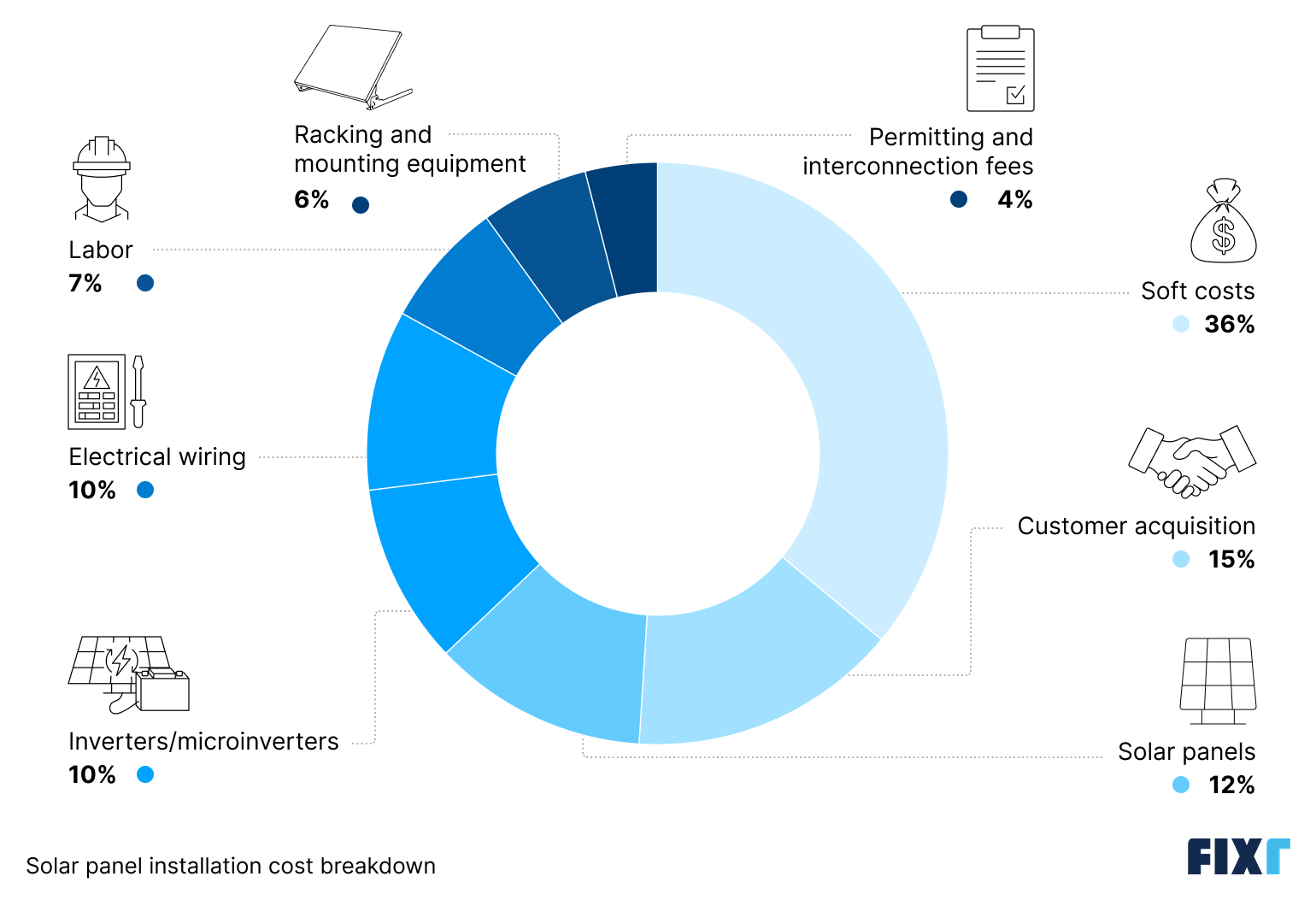
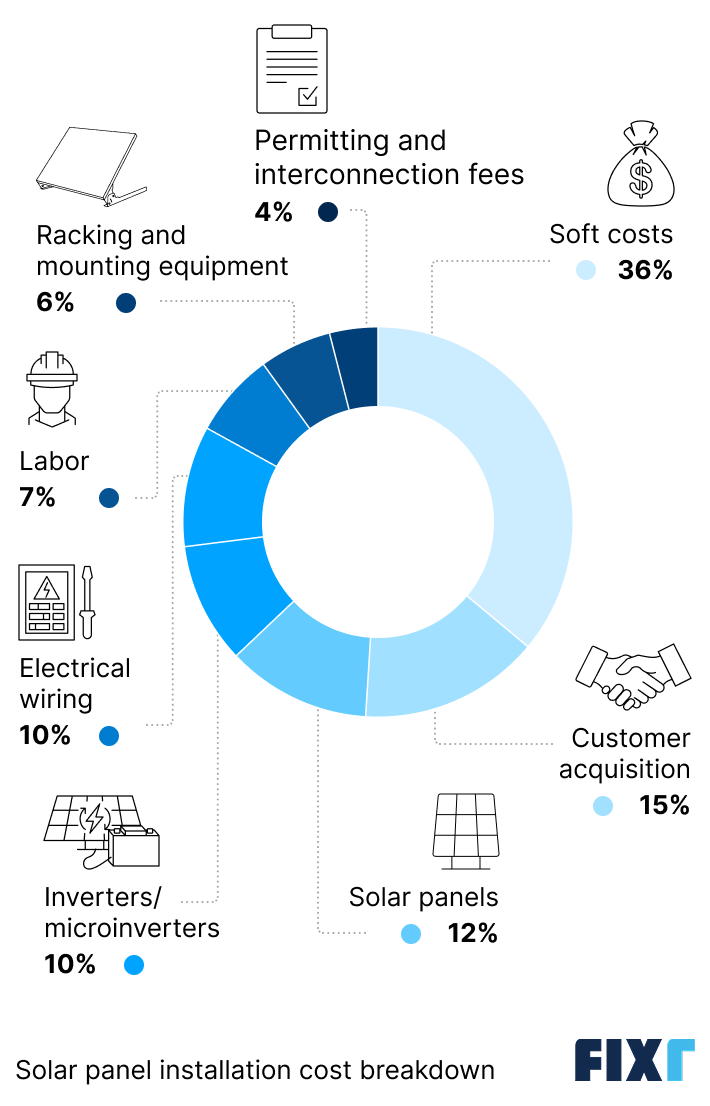
A lot goes into pricing solar energy systems, and while the panels themselves can be expensive, they only make up an average of 12% of your total. Most of what you pay goes toward equipment, labor, and soft costs.
Beyond the panels, your system includes inverters or microinverters (which convert DC power into usable AC electricity), mounting hardware, and wiring to connect everything to your home.
Soft costs cover items like permits, inspections, utility interconnection fees (if required), and installer overhead and profit. Labor costs also vary by location and can significantly affect your final price.
Item | Percentage of Cost |
Permitting and interconnection fees | 4% |
Racking and Mounting Equipment | 6% |
Labor | 7% |
Electrical Wiring | 10% |
Inverters/microinverters | 10% |
Solar panels (modules) | 12% |
Customer acquisition | 15% |
Other soft costs | 36% |
*calculated for a 7.6kW solar system
Solar Panel Cost by System Size
System size is one of the biggest factors affecting your solar installation cost. It’s measured in kilowatts (kW) and is based on your household’s energy consumption. On average, solar systems cost about $3.04 per watt, though larger systems often have a lower cost per watt. You can use the table below to estimate total costs based on different system sizes.
Keep in mind that accurate sizing matters. An undersized system may not cover your energy needs, while an oversized system can increase upfront costs without adding meaningful savings.
Sizing depends on many factors, including consumption habits, home energy efficiency, the climate in your area, your roof size, and even the direction your home faces. You should always hire a professional to determine what size solar array you need, but you can also use the National Renewable Energy Laboratory’s (NREL) calculator for a good estimate on system size.
System Size (kW) | Average Cost Before Incentives | Average Cost After Incentives |
3 | $9,100 | $6,400 |
4 | $12,200 | $8,500 |
5 | $15,200 | $10,600 |
6 | $18,200 | $12,800 |
7 | $21,300 | $14,900 |
8 | $24,300 | $17,000 |
9 | $27,400 | $19,200 |
10 | $30,400 | $21,300 |
11 | $33,400 | $23,400 |
12 | $36,500 | $25,500 |
13 | $39,500 | $27,700 |
Average Cost of Solar Panel Installation by Location
Residential solar installation costs vary widely from state to state due to differences in electricity rates, sunlight exposure, and local climate, all of which affect system size and overall pricing.
Solar panel installation costs can also vary between cities within the same state. Local labor rates, permit fees, utility-specific incentives, and regional supply and demand for solar equipment and installers can all push prices higher or lower.
State | Average System Size (kW) | Average Cost Before Incentives | Average Cost After Tax Credit | Average Solar Panel Cost per Watt |
Alabama | 5.8 | $21,047 | $14,733 | $3.42 |
Alaska | 5.1 | $19,084 | $13,359 | $3.52 |
Arizona | 7.0 | $20,759 | $14,531 | $2.79 |
Arkansas | 8.1 | $22,554 | $15,788 | $2.63 |
California | 5.9 | $20,840 | $14,588 | $3.33 |
Colorado | 4.9 | $17,799 | $12,459 | $3.41 |
Connecticut | 7.0 | $21,826 | $15,278 | $2.93 |
Delaware | 7.7 | $24,065 | $16,846 | $2.94 |
District of Columbia | 6.0 | $22,457 | $15,720 | $3.53 |
Florida | 8.4 | $23,351 | $16,346 | $2.61 |
Georgia | 6.3 | $21,166 | $14,816 | $3.17 |
Hawaii | 5.1 | $16,936 | $11,855 | $3.13 |
Idaho | 6.3 | $20,553 | $14,387 | $3.08 |
Illinois | 7.3 | $24,265 | $16,986 | $3.14 |
Indiana | 8.7 | $28,960 | $20,272 | $3.14 |
Iowa | 8.7 | $25,661 | $17,963 | $2.77 |
Kansas | 8.9 | $28,039 | $19,627 | $2.97 |
Kentucky | 7.3 | $21,173 | $14,821 | $2.74 |
Louisiana | 5.0 | $17,894 | $12,526 | $3.37 |
Maine | 7.7 | $25,348 | $17,744 | $3.10 |
Maryland | 8.2 | $25,372 | $17,760 | $2.91 |
Massachusetts | 7.3 | $24,221 | $16,955 | $3.12 |
Michigan | 6.5 | $23,669 | $16,568 | $3.44 |
Minnesota | 7.6 | $23,900 | $16,730 | $2.96 |
Mississippi | 5.2 | $17,284 | $12,099 | $3.14 |
Missouri | 10.9 | $31,032 | $21,722 | $2.68 |
Montana | 7.1 | $21,957 | $15,370 | $2.91 |
Nebraska | 8.9 | $26,294 | $18,406 | $2.79 |
Nevada | 7.2 | $21,745 | $15,222 | $2.85 |
New Hampshire | 7.8 | $24,627 | $17,239 | $2.97 |
New Jersey | 7.5 | $24,857 | $17,400 | $3.12 |
New Mexico | 5.2 | $17,251 | $12,076 | $3.12 |
New York | 6.9 | $24,479 | $17,135 | $3.33 |
North Carolina | 7.0 | $23,000 | $16,100 | $3.10 |
North Dakota | 10.8 | $35,906 | $25,134 | $3.13 |
Ohio | 7.2 | $22,209 | $15,546 | $2.90 |
Oklahoma | 7.0 | $19,618 | $13,733 | $2.64 |
Oregon | 5.9 | $19,963 | $13,974 | $3.18 |
Pennsylvania | 7.8 | $25,633 | $17,943 | $3.10 |
Rhode Island | 6.4 | $20,680 | $14,476 | $3.04 |
South Carolina | 7.6 | $24,663 | $17,264 | $3.06 |
South Dakota | 8.0 | $23,562 | $16,493 | $2.78 |
Tennessee | 6.7 | $21,198 | $14,839 | $2.97 |
Texas | 7.1 | $21,460 | $15,022 | $2.85 |
Utah | 5.8 | $19,637 | $13,746 | $3.19 |
Vermont | 11.2 | $33,301 | $23,311 | $2.79 |
Virginia | 6.9 | $22,346 | $15,642 | $3.05 |
Washington | 7.1 | $24,160 | $16,912 | $3.20 |
West Virginia | 8.4 | $25,154 | $17,608 | $2.83 |
Wisconsin | 7.0 | $22,401 | $15,681 | $3.01 |
Wyoming | 6.9 | $23,299 | $16,309 | $3.18 |
Key Factors Affecting Solar Panel Installation Cost
While system size is usually the biggest pricing factor, several other variables affect how much you’ll pay for solar. Below are the main considerations that determine your final installation cost.
Home Size
Larger homes typically require larger solar systems to offset electricity use, which increases installation costs. Household size, energy habits, and home efficiency also influence how big your system needs to be. A professional installer can assess these factors to determine the right system size for your home.
Climate
Climate affects both energy consumption and solar production. Hot climates often mean higher electricity use due to air conditioning, while colder regions typically rely less on electric heating. Sun exposure also matters, as homes in sunnier areas may need fewer panels, while cloudy regions often require larger systems to achieve the same output.
Type of Panel
Most residential systems use monocrystalline panels, but several panel types are available, each with different costs and performance:
Monocrystalline: Highest efficiency and most common for whole-home systems, but also the most expensive. Advanced technologies like TOPCon and PERC can increase costs further.
Polycrystalline: More affordable but less efficient, making them better suited for smaller installations.
Thin-film: Lowest cost and flexible design, but very low efficiency, typically used for RVs or small-scale applications rather than full homes.
A solar professional can help determine which option makes the most sense for your energy needs.
Roof and Home Characteristics
Roof orientation affects how much electricity your panels can produce, with south-facing roofs generating the most power in the U.S. Complex roof designs or limited usable space may require additional panels or reduce total output, impacting both installation cost and long-term savings.
Add-ons
Extras like solar batteries and EV chargers can significantly increase project costs. Solar batteries typically range from $7,000 to $18,000+ (around $15,000 on average), while EV chargers add roughly $600 to $2,000. These upgrades increase upfront costs but can add long-term value and convenience.
Purchasing Method
How you plan on paying for your panels can affect both your upfront and long-term costs. Paying in cash usually results in the lowest total cost and fastest payback. Financing reduces upfront expenses but increases long-term costs due to interest and potential origination fees.
Note that some less reputable installers charge origination fees that can further increase the cost of a financed system, and others charge higher fees for systems purchased with cash to maximize profit.
The Installer
Labor rates, system design fees, and profit margins vary by installer. Companies also differ in the brands they offer, which can affect both material quality and total pricing.
Solar Incentives & Savings
Solar is expensive, but incentives like tax credits, rebates, and production perks can all bring down your upfront costs and help increase your net savings over time. Solar incentives are a crucial part of making solar affordable, so make sure you take advantage of all of the savings you can.
We’ll include some of the more common incentives below, but you can also speak with your installer about local incentives or check the Database of State Incentives for Renewables and Efficiency (DSIRE) for more information for your area.
Federal Solar Tax Credit (ITC ended 2025): Homeowners who completed installations by December 31, 2025, could claim up to 30% of total system costs. This incentive no longer applies to systems installed in 2026 or later. Third-party owned systems (such as PPAs) may still qualify under commercial credits.
State & local solar incentives: Many states, cities, and utility companies offer rebates or tax credits that can help reduce upfront costs, depending on where you live.
Net Energy Metering (NEM): Earn credits for excess electricity your panels produce and use them later when your system underproduces. Compensation rates vary by utility.
Property tax exemptions: Installing solar increases your home's value, according to studies conducted over the past decade by SolarReviews, Zillow, and the Berkeley Lab. Home improvements that increase property value usually drive up property taxes, too, but many states and municipalities have property tax exemptions that prevent taxes from going up as a result of going solar.
Sales tax exemptions: Some states and townships waive sales tax on solar equipment, which helps reduce all-in material costs for installers and, as a result, individual solar customers.
Solar Renewable Energy Certificates (SRECs): In certain states with renewable portfolio standards (RPS), homeowners earn SRECs based on how much electricity their system produces. These certificates can be sold to utilities that need to meet clean energy requirements, providing ongoing savings or additional income. Availability and payout rates vary by state.
You can also save money on your solar panel installation by getting at least three quotes, comparing based on value, and choosing a reliable installer who will size your system appropriately. Additionally, investing in home energy efficiency improvements can mean smaller system requirements, which can bring down installation costs.
Solar Panel Financing Options
There are four primary ways to finance your solar panel installation: a cash purchase, a solar loan, a lease, and a power purchase agreement (PPA).
Cash purchase: Paying in cash requires covering the full system cost upfront, and many installers ask for up to 50% down to begin design and permitting, with the remainder due before activation. While this option has the highest initial expense, it offers the fastest payback and highest lifetime savings since there’s no interest and you fully own the system.
Solar loan: A solar loan is the most popular financing option for solar because it’s more accessible. You only need a small down payment or, in some cases, no money down to get your system installed. You’ll then pay off the remaining cost of the system plus interest over the loan term, which can range from 2 to 20 years or more. The interest will add to your all-in solar panel installation costs and reduce your net savings.
Solar lease: With a lease, you pay nothing upfront and instead make monthly payments to rent the panels. You benefit from the electricity produced, but you don’t own the system, and long-term savings are typically lower.
Power Purchase Agreement (PPA): A PPA also requires no upfront payment. Instead of renting the panels, you agree to buy the electricity they generate at a set rate. PPAs can reduce short-term energy costs, but ownership stays with the provider, limiting long-term savings.
Are Solar Panels Worth It? (ROI & Long-Term Value)
Solar panels are generally a worthwhile investment, with their value depending on factors like upfront cost, local electricity rates, household energy use, and how you pay for the system. Beyond sustainability benefits, solar provides greater energy independence, protection from rising utility prices, and the option to add battery storage.
Many installers estimate payback periods and lifetime savings to help homeowners evaluate returns. In the U.S., the average solar payback period is about 10 years, with typical ROI around 10%, and systems are considered worthwhile when lifetime savings are positive. When deciding, compare your current energy bills with projected solar costs and long-term savings. Solar may be less beneficial in areas with low electricity prices, homes with north-facing roofs, heavy shading, or roofs nearing replacement. Local incentives, especially net metering, also play a major role, as savings can drop significantly without them.
Are There Hidden Costs of Going Solar
There are some “hidden” costs of going solar that you should consider before you take the plunge. In some cases, you won’t see any hidden fees, but you may want to budget extra for these unexpected costs.
Roof condition and repairs: Your roof needs to be in good condition and should have at least 10 years of life left before installing solar. If repairs or replacement are needed, costs can increase by thousands.
Panel removal and reinstallation: If you replace or repair your roof later, panels must be removed and reinstalled, which typically costs around $3,800 unless covered by a lease or PPA.
Electrical upgrades: Older homes may need a 200-amp service upgrade or additional wiring, especially if adding an EV charger. These upgrades can add significant costs.
Monitoring system fees: Optional professional monitoring may come with monthly or annual charges.
Homeowners insurance increases: Because solar raises home value, insurance premiums may increase to reflect the added coverage.
Maintenance and cleaning: Panels usually need little upkeep, but homes in dry or dusty areas may require one or two professional cleanings per year.
Early lease termination fees: Some leases charge penalties if you exit the contract early.
Loan origination fees: Certain installers add financing fees to solar loans, increasing total system cost.
Escalating lease or PPA payments: Lease and PPA agreements may include built-in annual payment increases, which can reduce long-term savings.
DIY Solar Panel Installation vs. Hiring a Professional
While about $1,600 of a typical solar installation goes toward labor, total soft costs like design fees, permitting, and company overhead often push that figure closer to $13,400. That price difference can make DIY solar feel tempting, but installing solar panels yourself is rarely worth the risk.
DIY installations come with serious downsides, including safety hazards from working on your roof and handling electrical wiring, increased risk of fires and roof leaks, and the possibility of voided equipment warranties. Many local governments also require licensed professionals for solar installations, and homeowner’s insurance may not cover damage caused by DIY work.
Hiring a professional ensures your system is properly sized, safely installed, and fully permitted, making it the smarter long-term investment.
When looking for a solar installer, always confirm that the company is licensed and insured, and read through company reviews to see what other homeowners thought about the process. It’s a good idea to get at least three quotes from companies that seem reliable and then compare based on value, customer reviews, warranty coverage, cost, and equipment and service options.
FAQs
The average cost to install solar panels on a home is about $23,100, with most systems ranging from $19,100 to $23,800. Final pricing depends on factors like system size, energy needs, available incentives, add-ons, and local labor rates, so getting a personalized quote is the best way to estimate your costs.
Since the average U.S. home is close to 2,000 square feet, solar costs for homes this size are often near the national average of $23,100. However, square footage alone doesn’t determine system size; energy usage, roof layout, and sun exposure also play major roles.
In many cases, yes. Homeowners can save thousands (or more) over the life of their system. Whether solar makes sense for you depends on system size, energy bills, incentives, and how you pay for the installation.
Key cost drivers include household electricity use, roof size and orientation, climate, heating and cooling systems, equipment choices, and local labor rates. Because so many variables affect pricing, a professional site evaluation is the most reliable way to determine your total cost.
